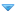
Currently Sentora sets all vhosts permissions to 777 apache:apache user for all vhosts.
This is not what is should be... we should take advantage of linux permissions properly. Also this method makes suhosin less important than it is right now in Sentora. As I see it right now, any bug in suhosin extension, or misconfiguration can potentially make every Sentora user be able to take control of a whole bunch of stuff... suhosin is just too important in sentora right now, and it seems they are not really fast to release extensions too so we do not have any PHP7 support yet...
I would like to see this method implemented in sentora to setup vhosts, its quite simple and effective :
The main features of this setup are the following:
Each user has his own home directory
Each user can have one or more websites hosted
Web server does not need extra configuration regarding users, groups etc.
Users are owners of their website(s) and can connect and modify their sites at will.
Users can only view the web directories that they own.
Simple and fast setup
Steps
Login as root
sudo su -
Create user with his own home dir
useradd -s /bin/bash -m -d /home/<username> <username>
Assign a password to the user
passwd <username>
Create virtual host's directory and set permission to user and group.
mkdir -m o-rwx /var/vhosts/<site>
Change ownership of vhost directory
chown -R <username>:<username> /var/vhosts/<site>
Add apache user www-data to user's group
usermod -a -G <username> www-data
The statement above gives apache web server the required permissions in order to run effectively all of the user's websites.
Check the groups that the user www-data belongs to:
root# groups www-data
www-data : www-data <username> ...
Create virtual host or virtual directory apache configration
Virtual directory setup
Alias /<subsite> /var/vhosts/<site>
<Directory /var/vhosts/<site>
Options None
AllowOverride All
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
</Directory>
Virtual host setup. Let's assume <site> is example.com. A sample config virtual host config could be similar to the configuration below:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
DocumentRoot /var/vhosts/example.com
ServerName www.example.com
<Directory />
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
</Directory>
<Directory /var/vhosts/example.com>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks MultiViews
AllowOverride All
Order allow,deny
allow from all
</Directory>
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/example.com.access.log combined
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/example.com.error.log
# Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit,
# alert, emerg.
LogLevel warn
</VirtualHost>
Reload/Restart apache
service apache2 reload
In case reload doesn't work (although it should) try restart:
service apache2 restart
Ready!
This is not what is should be... we should take advantage of linux permissions properly. Also this method makes suhosin less important than it is right now in Sentora. As I see it right now, any bug in suhosin extension, or misconfiguration can potentially make every Sentora user be able to take control of a whole bunch of stuff... suhosin is just too important in sentora right now, and it seems they are not really fast to release extensions too so we do not have any PHP7 support yet...
I would like to see this method implemented in sentora to setup vhosts, its quite simple and effective :
The main features of this setup are the following:
Each user has his own home directory
Each user can have one or more websites hosted
Web server does not need extra configuration regarding users, groups etc.
Users are owners of their website(s) and can connect and modify their sites at will.
Users can only view the web directories that they own.
Simple and fast setup
Steps
Login as root
sudo su -
Create user with his own home dir
useradd -s /bin/bash -m -d /home/<username> <username>
Assign a password to the user
passwd <username>
Create virtual host's directory and set permission to user and group.
mkdir -m o-rwx /var/vhosts/<site>
Change ownership of vhost directory
chown -R <username>:<username> /var/vhosts/<site>
Add apache user www-data to user's group
usermod -a -G <username> www-data
The statement above gives apache web server the required permissions in order to run effectively all of the user's websites.
Check the groups that the user www-data belongs to:
root# groups www-data
www-data : www-data <username> ...
Create virtual host or virtual directory apache configration
Virtual directory setup
Alias /<subsite> /var/vhosts/<site>
<Directory /var/vhosts/<site>
Options None
AllowOverride All
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
</Directory>
Virtual host setup. Let's assume <site> is example.com. A sample config virtual host config could be similar to the configuration below:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
DocumentRoot /var/vhosts/example.com
ServerName www.example.com
<Directory />
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
</Directory>
<Directory /var/vhosts/example.com>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks MultiViews
AllowOverride All
Order allow,deny
allow from all
</Directory>
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/example.com.access.log combined
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/example.com.error.log
# Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit,
# alert, emerg.
LogLevel warn
</VirtualHost>
Reload/Restart apache
service apache2 reload
In case reload doesn't work (although it should) try restart:
service apache2 restart
Ready!